OVERVIEW
Prostate Cancer occurs when prostate gland cells start to grow uncontrollably, the prostate gland is found only in men, it makes fluid of semen. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a substance which is produced by the prostate gland, Examining PSA level may indicate prostate cancer, infection or an enlarged prostate.
The normal value of PSA is 4 ng/ml if it is 4-10 ng/ml prostate cancer is doubtful when a value is > 10 ng/ml possibility of cancer is high.
Causes or Reasons
Like all types of cancer, clear reasons of prostate cancer is not available, in maximum cases multiple factors could be involved, as genetics, exposure to environmental toxins, certain chemicals or radiation. There are some risk factors for prostate cancer:
- Family History
- Age
- Race
- Geographical reason
- Diet
Symptoms
It is said by many patients that none of the symptoms have been noticed by them at earlier stages of prostate cancer:
If symptoms appear, some of them are the following:
- Urge to urinate often
- Decrease flow of urine
- Painful urination and ejaculation
- Blood in urine
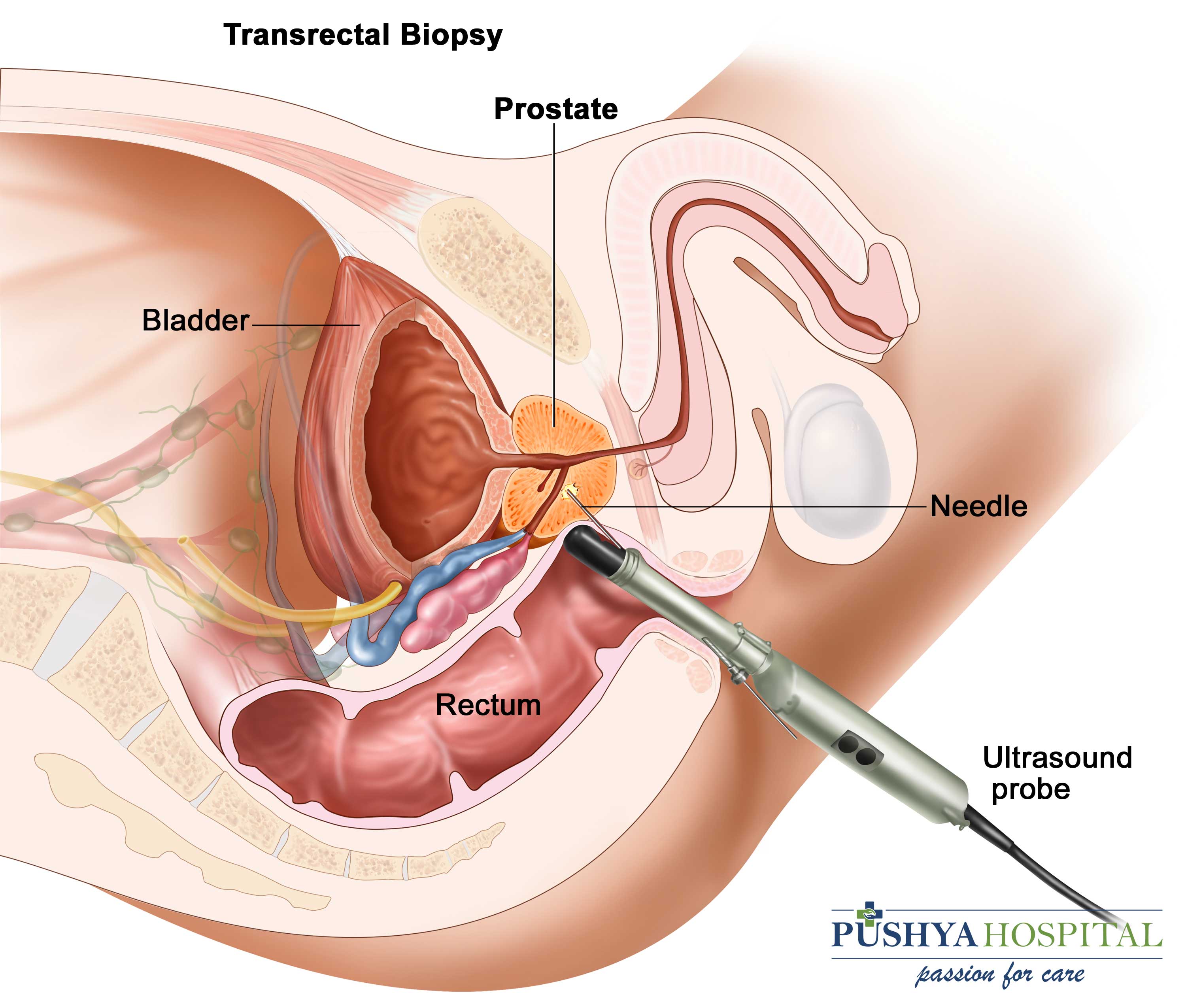
How we can evaluate (investigation)
Some options are available for confirmation of Prostate cancer
- Clinical diagnosis
- CT Scan/MRI
- Prostate Biopsy
- Bone scan
Treatment Options
Treatment options always vary on stage, age and overall health of a patient, At Pushya Hospital, urologists take care of specific needs and suitability of treatment options for prostate cancer patient, some of the treatment options we serve those are:
Active surveillance or waitful watching: Active surveillance demands close monitoring of cancer, this approach includes examination as prostate-specific antigen(PSA) blood test and digital rectal exam (DRE) after short time periods. A waitful watching approach is less intensive follow up, it includes fewer tests and relying more on changes.
Radiotherapy: If cancer has been spread outside the prostate gland or into nearby tissues or if cancer has comes back after prostate surgery or to keep cancer under control , Radiotherapy is suggested as a cancer treatment. There are two types of Radiotherapy:
- External Beam radiation therapy (EBRT): This type of radiation is suitable in earlier stages of cancer or to help relieve symptoms as bone pain. In EBRT radiation beams is applied from a machine outside the body.
- Brachytherapy or seed implantation: In this radiotherapy small radioactive pellets or seeds are used which have the size of grain or rice. These pellets are placed directly into the prostate. This radiotherapy is generally used for early-stage prostate cancer or when it is used in a combination of external radiation.
Chemotherapy: If prostate cancer has spread outside the prostate gland and hormone therapy is not working on a particular case then chemotherapy may be advised by doctors. It uses (chemo) the anticancer drugs which injected into a vein or given by mouth. These drugs travel through the bloodstream and reach to distant organs.
Hormonal therapy: Hormone therapy is also known as androgen deprivation therapy(ADT), this therapy works to reduce androgen hormones. As androgens (testosterone and dihydrotestosterone) stimulate prostate cancer cells to grow, Hormone therapy works to lowering androgen levels and it makes prostate cancer shrink or grows more slowly.
Channel TURP: After general or spinal anesthesia- resectoscope is inserted into the tip of the penis and it extends through urethra and prostate area. This surgical process does not demand any incisions on the patient’s body. The surgeon uses resectoscope to cut or trim tissues from inside of prostate gland, it takes place slowly one small piece at a time. As small pieces are cut inside the prostate, irrigating fluid carries them in a bladder; these pieces are removed at the end of the operation.
Bilateral orchidectomy: Orchiectomy is a surgical procedure in which a surgeon removes one or both (bilateral orchidectomy) testicles. It is a part of hormone therapy for patients with prostate cancer, performs to decrease the level of the male hormone testosterone in the body, which is responsible for prostate cancer growth.
Radical Prostatectomy: Prostate gland is located just under the bladder, in front of the rectum. It indicatedwhen cancer is confined to the prostate. There are mainly two types of Radical Prostatectomy Open Prostatectomy and Minimally invasive procedure:
Open Prostatectomy: Open Prostatectomy is the traditional method of radical prostatectomy, in this surgical procedure surgeon makes an 8-10 inch incision vertically below the belly. Once the prostate area is exposed to the surgeon, the surgeon detaches prostate gland from the urinary bladder and urethra, keeping the motive in mind to end cancer but lesser damage to surrounding organs. Once the prostate is removed, the resected end of the urethra is attached to the neck of the bladder. The surgeon places a foley catheter to enable urine to drain during the healing process.
There are two types of minimal Prostatectomy:
Laparoscopic Prostatectomy:-In Laparoscopic Prostatectomy surgeon make more then one small incision across the belly. Surgical tools and camera inserted through incision and radical prostatectomy occurs outside the body. A surgeon may see and control the entire operation through the video screen.
Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: - Small incision takes place in the belly, surgeon control an advanced robotic system of surgical tools from outside the body. With the help of high tech interface, surgeon use natural wrist movement and 3D screen helps during the surgical procedure.



