Overview
Hypospadias is a common congenital urological disease, it could be left without treatment if the condition is not too bad. Doctors may suggest a surgery to fix the problem if needed. Urine and sperm travel through the urethra, that tube which opens at the tip of the penis. Boys who have Hypospadias have that opening on the underside of the penis. Depend on the location that where the opening is, it may be a reason for mild or more serious issues like redness or infection. There are three kinds, depending on urethra location
- Near the head of the penis
- Along shaft of the penis (mid shaft)
- Location at the penis and scrotum meet or the scrotum (penoscrotal)
- Genetics
- Fertility treatment
- Mother’s age and weight at the time of pregnancy
- Location of the urethra is on the underside of the penis, as opposed to the tip.
- A downward urinary spray
- Downward curve of the penis, called ‘chordee’
- A “hooded” appearance to the penis, because of extra foreskin on the top side
- Abnormal appearance of the tip of the penis (the glans)
- Many cases of Hypospadias demands surgery to move urethra and opening, this procedure includes straightening of the penis.
- For the surgical procedure surgeon uses skin from the foreskin or elsewhere from the body to repair the opening. There is no related danger to the baby; the intention is just to repair the opening.
- Children who have this surgical procedure are generally between 3 to 18 months old and anaesthesia is used before surgery.
- Hypospadias surgery can be done at any time whenever parents notice the problem.
Cause or Reasons
There is no surety about causes of hypospadias, however, some of the reasons are
Symptoms
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
Doctors can identify hypospadias by examining the baby’s penis. It could be grasped easily if the opening is at a wrong place.
In some of the cases, penis also curves in a downward arc, which doctors call chordee, it can be seen at the time of erection.
Treatment Options
For Hypospadias, surgical procedure take place as a treatment option, At Pushya Hospital experienced urologists carefully examine the children and then plan whole surgical procedure , so that there will be best expected results only.
Overview
PUV is one of the most common causes of severe types of urinary tract diseases in children. It is an abnormal condition of the urethra. Urethra is the tube which drains urine from the bladder to the outside of the body for elimination. Abnormality takes place when urethral valves, which are small leaflets of tissue, consist of a thin slit-like opening which hampers urine outflow. When a reverse flow of urine occurs it can affect all of the urinary tract organs as urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys, generally, these organs swell, causes’ tissue and cell damage. Level of urinary outflow obstruction will determine the severity of urinary tract problems.
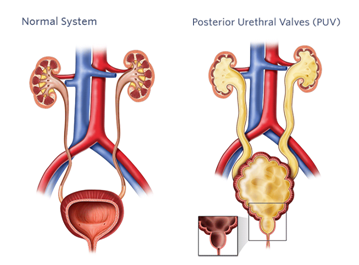
Cause or Reasons
- Children are born with extra flaps of tissue which cause this disorder; it cannot be always diagnosed at birth.
- It is an observation that parents do not pass this disease to their children but PUV has been seen in twins and siblings it looks like that there is a possible genetic component.
- The reason of tissue grow in the urethra is unknown, but it is believed early on in male fetal development.
- Normally, flaps of tissue in the urethra are very small structure, it is believed that during a fetus development the body sends signals which inform the tissue to stop growing or help tissue decrease in size
- In PUV, this signal which stops growth is thought to be missing and it causes tissue to keep on growing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of PUV can be noticed in different degrees from mild to severe. However, each child experiences different symptoms. Following are most common symptoms as
- An enlarged bladder which may be caught through abdomen as a large mass
- Urinary tract infection
- Painful urination
- Weak urine stream
- Urinary frequency
- Bedwetting or wetting pants after toilet training
- A problem in weight gain
- Difficulty with urination
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
- Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
- Direct endoscopic Visualization (cystourethroscopy)
- Blood tests as Creatinine
- Urodynamic study (UDS)
Treatment Options
At Pushya Hospital, we use specific and suitable surgical procedures and medications so that your child could go home free from his PU Valve, generally, our urologists use following for PU Valve treatment
Medicines - Medicines only, cannot work efficiently for treatment of PUV, medicines use additionally with a surgical procedure for severe problems, as in the case of severe hyperactivity of that muscle, which makes bladder muscle stiff. Anticholinergics/Antimuscarinics, Antispasmotics or sympathomimetics.
Surgery - In the maximum of the cases, PUV is treated with a surgical procedure called endoscopic incision of valves. It is also known as valve ablation or posterior urethral valve ablation, in this surgical procedure, the surgeon trims down the excessive tissue of valves. It is a minor and minimally invasive procedure and requires a small incision at the site of the ablation (removal ) of the valves.
When the child is in the impact of anesthesia, a surgeon inserts a small telescope called a cystoscope into the urethra. With the help of cystoscope, the surgeon could view the interior lining of the bladder and urethra on the monitor.
Now, the surgeon can use imaging to examine the obstruction and remove the valves.
- endoscopic incision of the valves, also known as valve ablation or posterior urethral valve ablation, is a surgical procedure that trims down the excessive tissue of the valves.
- This is a minor and minimally invasive procedure and only requires a small incision at the site of the ablation (removal) of the valves.
- While your child is under general anesthesia, doctors will insert a small telescope called a cystoscope into the urethra. With the cystoscope, doctors are able to view the interior lining of the bladder and the urethra on a monitor.
- Doctors will use the imaging to examine the obstruction and remove the valves.
Overview
Phimosis is condition seen in children, it is related with the foreskin of the penis. It is the condition when the foreskin of the penis cannot be pulled back (retracted) from the tip of the penis. Phimosis has been noticed as a common problem in young boys.
Cause or Reasons
Phimosis is the cause of tightening of an opening of the foreskin. This condition is considered normal for the newborn baby. With the time, the foreskin loosens and can be pulled down more easily. Generally, by the age of 17, most boys will be able to fully retract their foreskin. This problem can also occur if the foreskin is pulled forcefully before it is ready, it can cause the fibrous scar to form. It can keep the foreskin from retracting in future.
Symptoms
- Bulging of the foreskin at the time of urination
- Not able to fully retract the foreskin till the age of 3, in some boys it may take longer.
- Swelling of the tip of the penis, when the foreskin is pulled back
- Not able to pull the foreskin back over the tip of a penis.
- Tip of the penis in dark red or blue color.
- Making a small cut (incision) in the foreskin.
- A surgical procedure to remove all or some part of the foreskin for a child age 10 or older who complaint regarding bulging of the foreskin during urination.
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
Investigation for Phimosis include child’s physical examination, this physical examination includes penis and foreskin.
Treatment Options
At Pushya Hospital we prefer surgical treatment for phimosis. In children general anesthesia and in elder patients spinal aneasthesia is preferable.
Overview
An undescended testicle (cryptorchidism) is a testicle which does not move into its proper position in beg of skin, hanging below the penis before birth. In these cases usually one testicle is affected, but in some chances both testicles are undescended. This condition is not a very general one but common among premature baby boys. Usually, the undescended testicle moves into the proper position of its own, in some months after birth. If it do not happen naturally then surgery can relocate a testicle into the scrotum.
Cause or Reasons
An exact reason for the undescended testicle is not known but a combination of genetics, maternal health, and other environmental factors may affect or disrupt hormones. Physical changes or nerve activity also influence the development of testicles.
Risk factors for lower birth weight, premature birth, family history, conditions in which fetus growth effects as abdominal wall defect, smoking or alcohol usage or parent's exposure to some pesticides.
Symptoms
An undescended testicle can be identified during after birth examination. If the testicle is not moved into the scrotum till 4 months of birth, the problem probably would not correct itself. Treating this condition at an early age lowers risk of complications later in life as infertility and testicular cancer.
From infants to pre-adolescent boys- who have normally descended testicles at birth could be with “missing” a testicle later. This condition may be as
- A retractile testicle, which moves back and forth between scrotum and groin, it could be in the condition to manage into the scrotum during a physical examination, this condition is not abnormal and because of muscle reflex in the scrotum.
- An ascending testicle, or acquired undescended testicle, which has “returned” to a groin and cannot be managed by hand into the scrotum.
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
Laparoscopy:- A small tube which contains a camera is inserted through the small incision in the baby’s abdomen. Laparoscopy is done to check an intraabdominal testicle. There are chances that doctor can fix undescended testicle in this surgical procedure but an additional surgery could be necessary according to the case.
In other cases, laparoscopy might show no testicle present or a small remnant of which have nonfunctioning testicular tissue than it could be removed.
Open surgery - Direct examination of abdomen or groin through larger incision may be necessary in some cases.
If after birth it remains difficult to detect any testicles in the scrotum, further testing could be done.
Treatment Options
Surgery
An undescended testicle is generally corrected with surgery, the surgeon carefully places correct testicle into the scrotum and stitches it (orchiopexy). This procedure can be done with both open and laparoscopic surgery. Child’s surgery depends on the number of factors as his health and how difficult would the procedure be. Surgery is preferable when the child is 6 months old and before completing 12 months. At this age surgical treatment has a lower risk of complications.
In the case when testicle is poorly developed, having abnormal or dead tissue, then the testicular tissue is removed during the surgical procedure.
If the child has an inguinal hernia associated with an undescended testicle, the hernia can be repaired during the surgery.
After surgery surgeon keeps monitoring on testicle for proper functioning and stays properly, it may include physical examination, ultrasound examination of scrotum and hormone level examination.
Overview
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction is a blockage in the territory which associates the renal pelvis (some portion of the kidney) to one of the tubes (ureters) that move urine to the bladder. In most of the cases, Ureteropelvic junction obstruction happens when a child is developing in the womb. This is known as an inherent condition (present from birth).
Cause or Reasons
More often, the blockage is caused when the association between the ureter and the renal pelvis does not grow ordinarily and makes urine develop, potentially harming the kidney. The condition can likewise be caused when a vein is situated in the wrong position over the ureter, causing a twist or kink in the ureter. In youngsters and grown-ups, ureteropelvic intersection check can be because of scar tissue, contamination, past medications for a blockage or kidney stones.
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction is the most analyzed reason for urinary impediment in kids. It is one of the most commonly done pre-birth ultrasound procedures. Sometimes, the condition is not noticed until after birth. Kids may have a stomach mass, urinary tract disease, or torment in the stomach or side.
Symptoms
- Abdominal, back, or flank pain (pain in the side)
- Blood in urine
- Lump in the abdomen (abdominal mass)
- Urinary tract infection which includes a kidney infection, where there is fever
- Inappropriate growth in infants (failure to thrive)
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
Ultrasound examination during pregnancy may reveal kidney problems in an unborn baby. However, there are some tests which include:
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to determine the degree of dilation or stretch of the kidney.
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to Nuclear scan of kidneys
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to Voiding cystourethrogram
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to Electrolytes
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to BUN
- Kidney ultrasound study – This examination is done to Creatinine
Treatment Options
Surgery takes place to correct the blockage which allows urine to flow normally and it can take place through open or laparoscopic methods. Both of the methods are called a pyeloplasty and it includes removing the abnormal part of a ureter and connecting it again to the kidney for a normal urine flow.
- In most of the cases of ureteropelvic Junction obstruction, surgery do not require at all, but checkups should be done periodically until obstruction has gone away, just most severe cases demand surgery.
- Open surgery can be performed at all ages, it involves an incision at side or back so that blockage could be removed and repair ureter.
- Laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive technique can be used at all ages. This surgery involves the assistance of robotic surgery in this delicate repair.
Open and laparoscopic surgery both have the similar success rate, but laparoscopic procedure allows to return home sooner in the comparison of open surgery.
Overview
Vesicoureteral reflux is the abnormal flow from your bladder back up the tubes (ureters) which connects kidneys to the bladder. Normally, urine flows only down from the kidneys to the bladder. This problem is usually diagnosed in infants and children. This disorder of urine flow, increase the risk of urinary tract infections, which can lead to kidney damage.
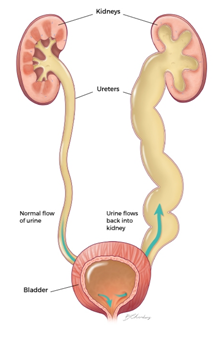
Cause or Reasons
- Bladder and bowel dysfunction (BBD) - Children with BBD hold their urine and stool and may have recurrent urinary tract infections, it can be a direct reason for vesicoureteral reflux
- Race - White children have higher risks of vesicoureteral reflux.
- Sex - Girls, have double chances of having this condition, than boys.
- Age- There are more chances to have vesicoureteral reflux in infants and children up to the age of two.
- Family History - Primary vesicoureteral reflux tends to run in families. If parents had then there are more chances of disease in the next generations.
Symptoms
- Strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Abdominal or flank pain
- Hesitancy to urinate
Infants may have a fever in the condition of Vesicoureteral reflux, it is the common symptom in them:
- If a baby is younger than 3 months and has a rectal temperature of 100.4 F or higher.
- Is 3 months or older and have a fever of 102 for higher without explainable factors, as recent vaccination or cold.
- Change in appetite
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
- Kidney and bladder ultrasound
- Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
- Nuclear Scan
Treatment Options
At Pushya Hospital, we have urological experts, who can catch the issues with slight observation and prescribe the perfect solution for delicate children as:-
Medications - Doctors prescribe antibiotics with immediate effect to keep the infection in control from moving to kidneys. A child who is being treated with medication needs to be monitored as long as he/she is taking antibiotics. Monitoring includes periodic physical examination and urine tests so that your doctor could detect infections or UTIs. UTIs which occur despite the antibiotic treatment could be tracked with the help of radiographic scans of bladder and kidneys which ultimately turns vesicoureteral reflux.
Surgery - Surgery for vesicoureteral reflux repairs the defect in the valve between bladder affected ureter.
Open Surgery - Using Anesthesia, surgeon gives an incision in the lower abdomen, by which the surgeon repairs malformation which is the ultimate cause of a problem. This surgery demands a few days stay in the hospital, a catheter generally placed so that the bladder could be drained.
Robotic assisted laparoscopic surgery - This procedure also involves procedure of repairing valve between ureters and bladder as open surgery, but Robotic surgery uses small incision. This surgery includes some advantages as smaller incision and possibly less bladder spasm than open surgery. But not as successful as an open surgery however it includes longer operating time but a shorter hospital stay.
Endoscopic surgery - In this surgical procedure, the surgeon inserts a lighted tube (cystoscope) through the urethra to see inside the bladder, then injects a bulking agent around the opening of affected ureter so that surgeon could check and try to strengthen the valve’s ability to close properly.
When this surgical method is compared with open surgery and presents fewer risks and requires general anesthesia.
OVERVIEW
Megaureter is an abnormal condition of one or both ureters of the child. Ureters are two funnel-shaped tubes which carry urine from a kidney to bladder. A megaureter refers to an expanded or widened ureter which is not working normally. Usually, the size of a megaureter is greater than 10 millimeters in diameter.
Complications which are related with this disease include reverse flow of urine into the kidneys and pooling of urine inside ureter which does not drain. This pooling can cause a child to develop a urinary tract infection, which can lead to kidney damage and failure.
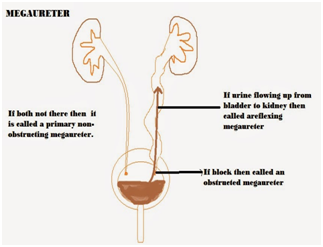
Cause or Reasons
A megaureter occurs during fetal development, it occurs when a section of ureters which is a normal muscular layer of tissue, is replaced by stiff, fibrous tissue. In the absence of muscular layer, normal peristalsis (worm-like movement of ureters which help to move urine toward bladder) cannot occur. Megaureter can occur alone but usually occurs in combination with other disorders, like prune belly syndrome.
Symptoms
Generally, megaureter can be detected on prenatal ultrasound but sometimes a child is referred to a pediatric urologist or pediatric surgeon after noticing one of the following symptoms during early childhood.
- Abdominal mass which can be seen or felt
- Pain in back or abdomen
- Urinary tract infection with fever
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Urinary Inconsistency
- Urolithiasis (stone formation with urinary tract)
How we can evaluate it (Investigation)
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
- Voiding Cystourethrogram
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Diuretic renal scan
- Blood tests
Treatment Options
At Pushya Hospital, we use specific treatment options perfectly suitable according the case, so that every child would be recovered from Megaureter. If the investigation proves a block or impaired kidney function, in this case, the child may be needed a surgery to fix it. Surgery for megaureter involves putting ureters back into the bladder (ureteral reimplantation) and trimming the widened ureter. If the child does not have a urinary tract infection, surgery can be delayed till the age of 12 months. Till that time antibiotics can be given to child to prevent infection.
Open Surgery - In the case of kidney function problem, open surgery requires an incision; it is one of the preferred surgical method. The surgeon makes a cut in the lower belly. Depends on specific condition, surgeon will get to the ureter either through bladder (transversal) or from outside the bladder (extravesical) and then removed.
If ureters are very wide, it may need to be trimmed (tapered) and blockage also can be removed.
For refluxing megaureters, the reflux (urine back-up) is corrected and for wide ureters, the ureters can be trimmed.
Baloon Dilation - Baloon Dilation
Laparoscopy surgery - This surgical procedure is done through thin tubes which insert by the surgeon through small cuts. For the procedure, the surgeon uses a special camera to see inside the body and miniaturized tools. This surgical procedure does not come in easy surgeries and requires highly skilled surgeons.



