OVERVIEW
The prostate gland or the prostate is an organ of the male reproductive system. It is located at the base of the bladder and has a size of a walnut, it produces alkaline fluids which nourishes and protect sperm cells.
Most two common forms of the prostate disease are inflammation (prostatitis), non- cancerous enlargement of prostate BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
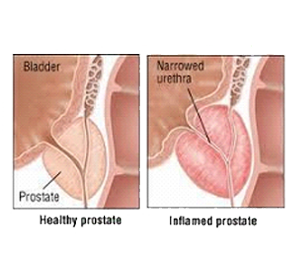
Prostatitis is a condition in which prostate gland suffers from swelling and inflammation. Depends on the cause, prostatitis can develop gradually or suddenly, in some cases, prostatitis stays for months or keep recurring, it is called chronic prostatitis.
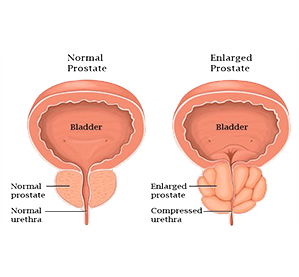
Your prostate surrounds part of the urethra, a tube which carries urine and semen out of the body, when you have BPH, prostate becomes larger than usual which squeezes the urethra, it becomes a reason of weak stream of urination.
PROSTATITIS BPH
SYMPTOMS OR SIGNS
Many of the times, a prostate disease may or may not indicate any symptoms. Some of the symptoms of prostatitis and BPH includes:-
PROSTATITIS
- Difficulties in urination as trouble starting
- Pain in groin, pelvic area or genitals
- Sometimes flu-like symptoms
- Cloudy urine or blood in the urine
- Painful ejaculation
BPH
- Urge to urinate especially at night
- Pain at urination
- Leaking or dribbling of urine
- Incontinence, no control on pee
- An urgent need to pee, suddenly.
REASONS FORPROSTATE DISEASE
PROSTATITIS
There are following examination ways to confirm kidney stone:-
- Elder age as 50, but many cases has seen in younger people also.
- Urinary tract or bladder infection
- Pelvis injury
- Old prostatitis or prostate biopsy
- HIV/AIDS
BPH
Following are some risk factors for BPH:-
- Hormonal changes, as you grow
- On the age of puberty prostate gland become double in the size, after 25 it grows again, for most of the males this growth remains for rest of the life, for some this growth becomes a reason of BPH.
- A family history of BPH
How we can evaluate (Investigation)
- Physical examination
- Some Blood tests
- PSA (Prostate specific antigen.
Some advanced tests as:-
- Ultrasound to measure size of Prostate and residual volume of urine
- Bladder ultrasound
Treatment options
PROSTATITIS
- Antibiotics: - If you have severe symptoms, you may be needed intravenous antibiotics, you may need to take oral medications for four to six weeks, it may be longer for chronic or recurring prostatitis.
- Alpha Blockers: - This medication helps to relax the bladder neck and nearby muscle fiber at that specific place where prostate joins the bladder, these antibiotics might give relaxation as in painful urination.
- Anti-inflammatory agents: - Some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug might be helpful in relaxation in painful symptoms of prostatitis.
- BPH : Your doctor may suggest you for some lifestyle changes and medicines to treat your BPH
- Medicines: - In mild to heavy BPH, doctors recommend medications, to relax muscles in your prostate and bladder and shrink prostate as well. Generally, doctors recommend a mix of medicines for maximum results.
- Prostate surgery: -If medications or other things do not respond well to you, the doctor may prescribe prostate surgery for the treatment of Prostatitis and BPH. Generally, these are “minimally invasive” surgical procedure; it does not require large cuts on your body. Minimal invasive surgery is easier than regular surgery.
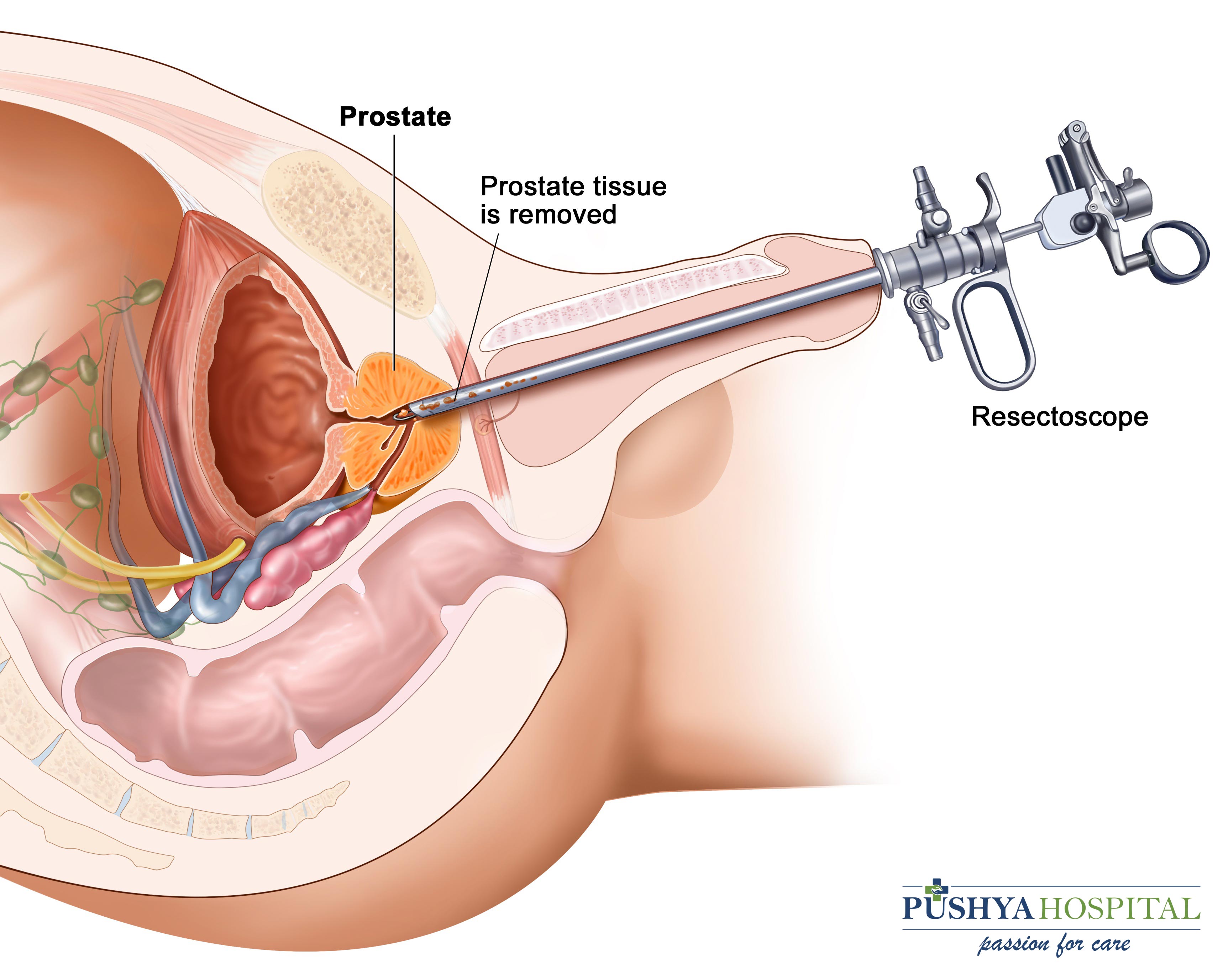
- 1. TURP: -It is endoscopic surgery of prostate that doesn`t require cut over the body. Three days hospitalization required and patient is discharged after removal of tube.
- 2. Laser prostatectomy : -It is also endoscopic surgery of prostate. Laser is a method of cutting of Prostate. Laser either to burn the prostate and complete removal of enlarged part of Prostate. In laser bleeding is less, chance of hyponatrimia are also less.



